Earlier issues of ElectronicsCooling showed the thermal conductivity for pure Si (May ’98), SiO2 (Aug ’04) and III-V semiconductors (Feb ’06). This column focuses on doped Si, porous Si and isotopically pure Si.
Table 1. Thermal Conductivity Data at Room Temperature
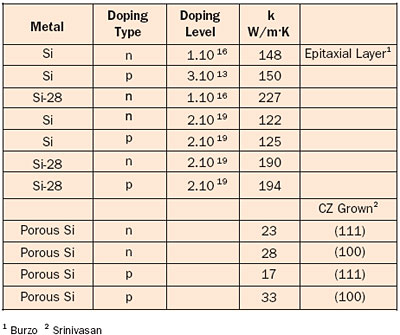 |
The first seven rows of Table 1 show thermal conductivity data for natural and isotopically pure Si as measured by Burzo et al. for low- and high-doping levels, both for n and p-type. The average error can be taken at 5%.
When Si is mentioned, natural Si is referred to in the overwhelming number of cases. Natural Si consists of three isotopes: Si-28 (92%), Si-29 (4.7%) and Si-30 (3.3%). By purification it is possible to acquire pure Si-28 that exhibits a significantly higher thermal conductivity, as is clear from the Table, at a significantly higher cost.
From the Table it can also be concluded that a significant difference exists between low- and high-doped Si. These recent results are in contrast with the results of Thompson and Younglove (1961) who found that there is almost no dependence of the thermal conductivity on the doping level above 100 K. Also Touloukian (1970), who collected the results from 80 studies, showed that 78 of them reported values in the range of 120-140 W/m�K at room temperature, independent of the doping level. Two studies for p-type Si with 5.1020 atoms/cm3 reported values between 40 and 80 W/m�K. However, for cryogenic temperatures below 40 K the differences are orders of magnitude larger. The reasons for the discrepancies are not clear but might be attributed to the manufacturing method, the thickness of the layers involved or, last but not least, the measurement technique.
The Table shows also some data for porous n and p-doped Si (grown using the Czochralski method) for two crystal orientations.
References
- Burzo, M., Komarov P., Raad, P., “Non-Contact Thermal Conductvity Measurements of p-Doped and n-Doped Gold Covered Natural and Isotopically Pure Silicon and Their Oxides,” Proceedings EUROSIME04, 2004, pp. 269-276.
- Touloukian, Y., Powell, R, Ho, C., Klemens, P., “Thermal Conductivity of Metallic Elements and Alloys,” IFI/Plenum, New York, 1970.
- Thompson, J. and Younglove, B., Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, Vol.20, 112, 1961, 146-149.
- Srinivasan, R., Jayachandran, M., Ramachandran, K., “Role of Doping on the Thermal Properties of Porous Silicon,” http://event.ua.pt/dsl2005/Srinivasan.pdf, 2005.






