AIR FORCE INQUIRES ABOUT THERMAL MGMT.SOLUTIONS FOR FUTURE AIRCRAFT
8/11/15 – The U.S. Air Force is looking into new thermal management techniques to cool the electronics in future fighter aircraft. “Officials of the Air Force Research Laboratory at Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, Ohio, issued a broad agency announcement Friday (BAA-AFRL-RQKP-2015-0002) for the Hybrid-Cycle Power and Thermal Management System (PTMS) project,” according to Military & Aerospace Electronics.
“The Air Force Research Lab’s Power and Control Division, Mechanical & Thermal Systems Branch are asking industry for electronics cooling ways to blend air-cycle cooling, vapor-cycle cooling, chilled fuel, and other thermal energy storage mechanisms to keep electronics cool on future jet fighters,” according to researchers.
Source: Military & Aerospace Electronics
3D WHITE GRAPHENE YIELDS FAN-FREE COOLING/THERMAL MANAGEMENT SOLUTIONS
7/20/15 – Researchers from Rice University have discovered that 3D White Graphene could help cool small-scale electronic devices by itself. When the research group completed simulations of heat flows through 3D white graphene structures, which are made of boron nitride, the normal 2D structure took the form of normal hexagonal structure of graphene. The team then investigated “how its natural heat conduction properties could be exploited in 3D arrangements.”
“Simulations show that 3D structures of white graphene-sheets of the 2D stuff held together with boron nitride nanotubes- quickly move heat in all directions. But they also show that by tuning the lengths and densities of the interconnecting tubes, the material can be tuned to channel heat in specific directions-shorter ones slow conduction, while longer ones speed it up,” according to Gizmodo. Even though the team’s research is solely based on simulations, they remain positive that this discovery will help introduce new kinds of 3D thermal management systems for small electronic devices in the near future.
Source: Gizmodo
CALIFORNIA ENERGY CODE UPDATED; NEW REGULATIONS FOR COOLING DATA CENTERS
7/28/15 – The California Energy Code, also known Title 24 of the CA Code of Regulations – part 6, has been revised. The new revision implements new regulations for cooling data centers and server rooms in order to improve efficiency, reduce daily operation costs, reduce carbon footprints and simplify cooling models. The new rules apply to computer rooms, which Title 24 defines as: “A room whose primary function is to house electronic equipment and that has a design equipment power density exceeding 20watts/ft² (215 watts/m²) of conditioned floor space.” The new requirements affect the way data centers are cooled. The new CA Title 24 Code Requirements include: economization, air-side economization, water-side economization, reheat prohibited, humidification, fan efficiency, fan control and air containment.
Source: Datacenter Journal
LEDS TO MOVE DATA FASTER IN ELECTRONICS
8/4/15 – University of Virginia engineering researchers have come up with a way for LEDS to move data to wireless devices faster. This process involves “using light waves from light-emitting diode fixtures to carry signals to wireless devices at 300 megabits per second from each light. It’s like having a whole wi-fi system all to yourself; using light waves, there would be more network access points than with radio waves, so less sharing of the wireless network,” according to researchers. “Visible light communications has the potential to significantly increase the speed of Internet connection in multiuser indoor environments due to the broad bandwidth of the visible light. It will offer a huge energy saving for the nation since energy is already used for lighting, and thus does not need to be expended for communications,” the team concluded.
Source: Phys.org
NEW MATERIAL DECREASES ENERGY USAGE IN ELECTRONICS
8/4/15 – Researchers have determined that gallium nitride (GaN) could become the next best semiconductor for electronics because it would immensely cut energy usage. Cambridge Electronics Inc. (CEI) has announced a new line of GaN transistors and power electronic circuits. This line promises to reduce energy usage by 10 to 20 percent in consumer electronics, data centers and electric cars by 2025. CEI plans to use these transistors to make data centers use less energy, electric cars more powerful and cheaper to build and power adapters one-third of the size, according to Phys.org.
Source: Phys.org
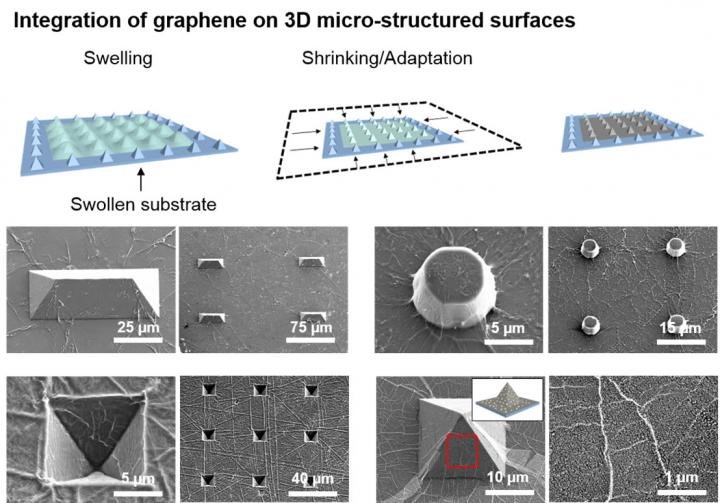
3D SHAPES FORMED FROM FLAT SHEETS OF GRAPHENE
3/9/15 – A team from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign has developed a new method for forming 3D shapes from flat 2D sheets of graphene. This development will pave the way for flexible electronics and integrated systems that are graphene and MEMS hybrid devices. Integrating 2-D graphene sheets onto 3D structured surfaces allows the graphene to hold its structure; however, the 3D features and dimensions vary from 3.5 to 50 μm.
Source: Science Daily
HPC NETWORKS SUCCESSFUL LIQUID COOLED FOR FIRST TIME
7/20/15 – Icetope, a company that specializes in the liquid cooling of electronics, announced it has successfully liquid cooled HPC networks. “Liquid cooling systems work by transferring all the heat directly into liquid. The waste heat is then removed in the form of hot water, which is pumped around the cabinet and can be re-purposed for domestic heating,” according to Electronics Weekly. The company developed a “fan-less Mellanox-based Inf iniBand and Ethernet network and interconnect switch for supercomputer (HPC) systems.”
Source: Electronics Weekly